Active Bass Control
Fulcrum One supports the configuration and calibration of an active bass control system when coupled with a Fulcrum Venueflex DSP processor. Fulcrum's Active Bass Control capability minimizes hot spots and power alleys in low-frequency coverage throughout a room and can compensate for room resonances and boundary effects in balconies or other challenging spaces.
We recommend reviewing the Design Guide for Immersive Systems for an overview of designing a system for active bass control.
Active Bass Control works by driving a network of subwoofers throughout a space with a custom-calibrated signal derived from the "subwoofer" or full-range mix signals being sent to the primary reinforcement or playback system. After the calibration process, the system uses FIR filters to create a custom signal for each subwoofer in the network.
Active Bass Control Settings
The project's Settings screen contains a number of controls for Active Bass Control. These settings are global and affect the measurement and calculation process when acquiring new FIR filters for active bass control. Note that the default settings are typically successful for most applications.
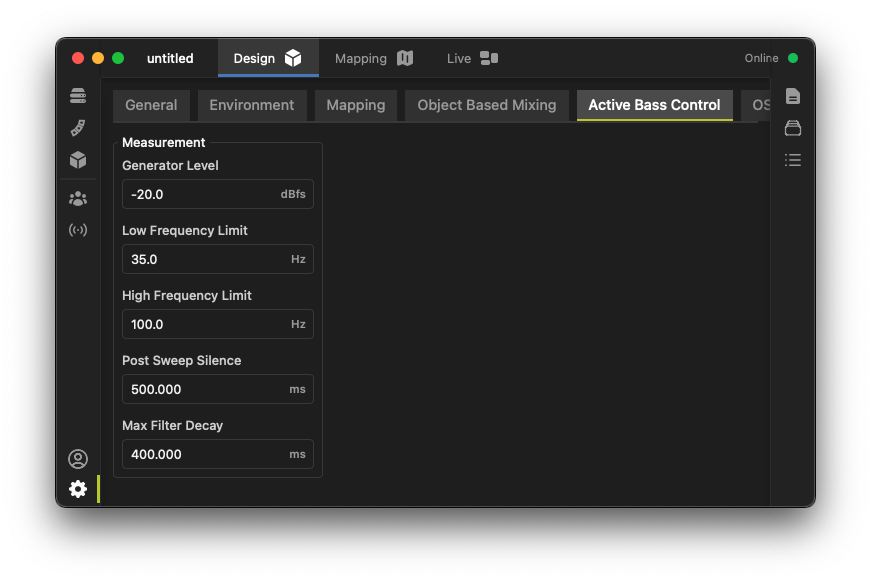
- Generator Level: During the measurement process, the system injects a full-bandwidth sinusoidal sweep into the system input paths as well as the individual feeds to the active bass control subwoofers. This setting chooses the level (in decibels relative to full scale) for that sweep signal.
- Low Frequency Limit: This is the lowest frequency processed by the active bass control system, selectable between 20 Hz and 50 Hz. This value should not be set lower than the low-frequency cutoff of the installed active bass control subwoofers.
- High Frequency Limit: This is the highest frequency processed by the active bass control system, selectable between 60 Hz and 120 Hz. Higher values can be used if the active bass control subwoofers are more closely spaced, which can be helpful in smaller rooms.
- Post Sweep Silence: This parameter is the generated silence at the end of the sweep signal in milliseconds. Higher values can be used for rooms with longer broadband reverberation times.
- Max Filter Decay: This is the maximum decay time of the FIR filters used in the active bass control system in milliseconds. Higher values can be used for rooms with longer low-frequency reverberation times.
Patching and Configuration
Once an engine in a project has been configured with Active Bass Control (see Adding Engines), a drop-down list for Active Bass Control will appear in the Engines toolbox with the selected number of subwoofer outputs. From this view, channels can be monitored, muted and configured.
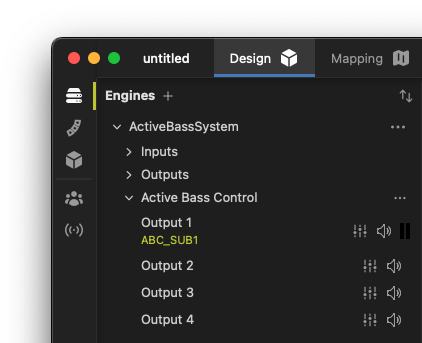
Click the ellipsis (...) to open the Active Bass Control Settings window for the selected engine. This window allows the user to configure the IO patching for the active bass control system, start calibration, and view the loaded FIR filters.
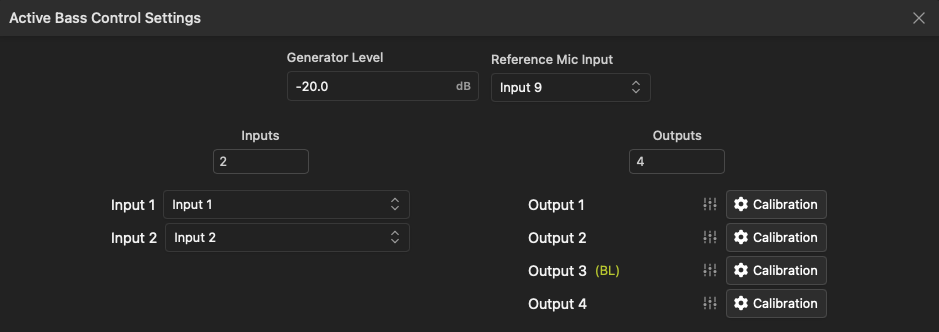
To ready the system for calibration, configure the following settings:
- Generator Level: Set the level for the sweep generator in decibels relative to full scale. Changes here will be reflected in the project settings window as well as the calibration windows.
- Reference Mic Input: Select a physical input channel that is connected to the measurement microphone that will be used for calibration.
- Inputs: Select the number of input channels the bass control module will process. This could be a single input (if a mono subwoofer feed is used) or more if compensating for multiple PA feeds. Select the associated input channels in the drop-down lists below. Note the inputs must already be routed to the appropriate output channels and the system should be "tuned" before calibration. Any additional changes to the system equalization, relative level or timing will require recalibration.
- Outputs: Select the number of active bass control subwoofer output channels the module will process. Associated subwoofer speaker channels can be selected in the Calibration window. Any channels already assigned to a speaker will appear beside the output number.
Calibration
To calibrate an individual subwoofer output, click the Calibration button beside the desired output number. This will open the Calibration window for that output.
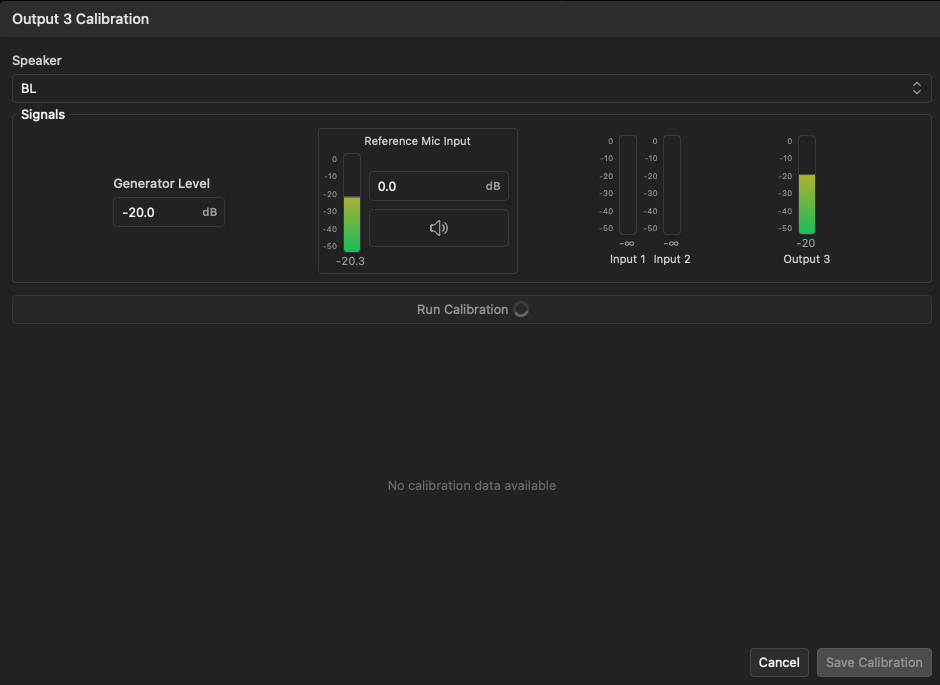
Follow these steps to calibrate the subwoofer output:
- In the Speaker drop-down menu, select the speaker name of the active bass control subwoofer that you wish to associate with this module output.
- If desired, adjust the generator level and attenuation of the reference microphone input.
- Place the measurement microphone physically near the subwoofer being calibrated, typically roughly 1 meter from the face of the driver. This may require the use of a tall stand, arm, or lift in some installations.
- Click the Run Calibration button to begin the calibration process. The system will inject a sweep signal into any input channels configured, as well as the selected subwoofer output, and measure the response with the reference microphone. You will hear a sweep for each input, plus one additional sweep for the subwoofer being calibrated. Do not move the microphone during this process.
- Once the calibration process is complete, the system will calculate FIR filters for the subwoofer output and display each filter in the window. The calibration process can be repeated as needed to refine the result. When satisfied, click the Save Calibration button to load and activate the filter into the active bass control system.
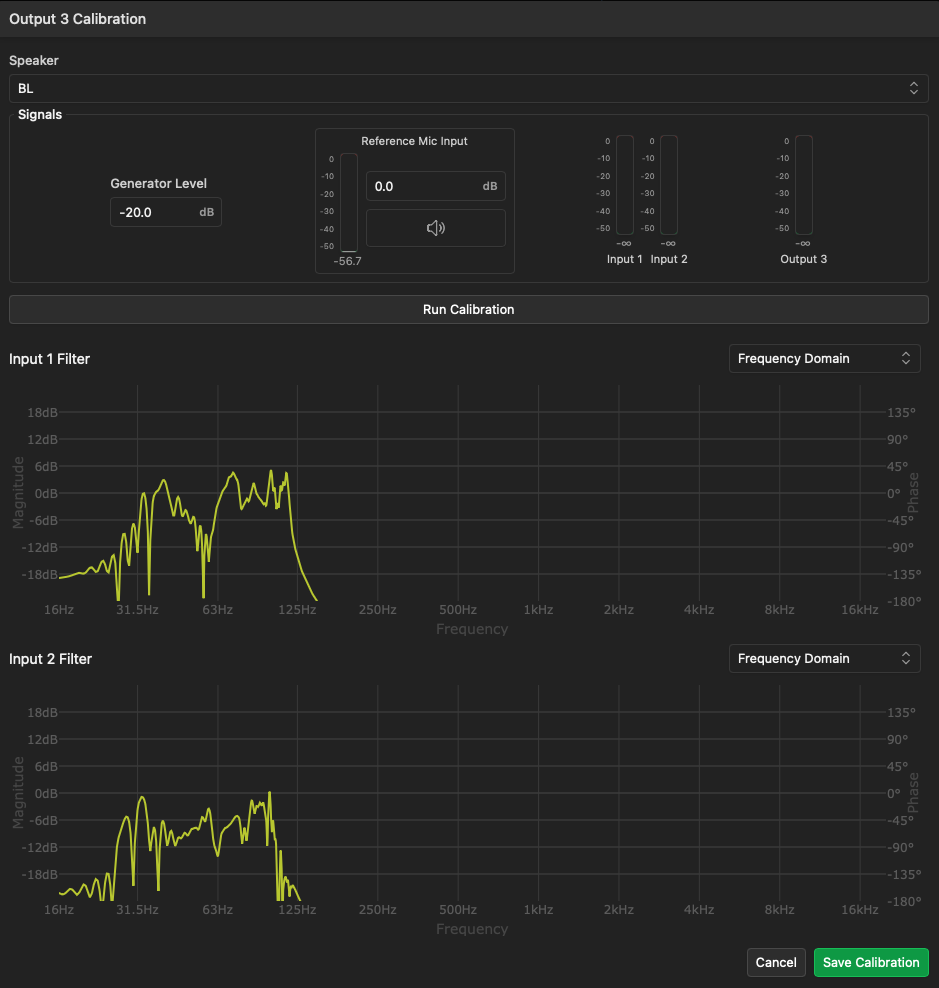
You may click the  button in the Engines list or the Active Bass Control Settings window to view the loaded FIR filter in either the time or frequency domain. From this window, you may also bypass or delete the filter or re-run the calibration process.
button in the Engines list or the Active Bass Control Settings window to view the loaded FIR filter in either the time or frequency domain. From this window, you may also bypass or delete the filter or re-run the calibration process.
